Thinking about leasing a car? There are a number of reasons why lease agreements win out when you’re trying to compare the benefits of leasing vs buying a car.
Car Leasing and Finance makes sense, when its understandable

When you lease a car, you don’t have to worry about depreciation, you can make a smaller down payment than is required when you purchase a car, and the payments are usually similar or less than the financing payments when you buy a car. But for all of the benefits of leasing, understanding a car lease can be difficult, as there are many related terms that you may never have encountered before.
In order to understand how to lease a car, you first need to have a working knowledge of these terms. This guide to car leasing terminology will teach the lingo that you need to master in order to understand your lease and make sure that you get a fair deal.
Search by letter:
A | B | C | D | E | F | G | H | I | J | K | L | M | N | O | P | Q | R | S | T | U | V | W | X | Y | Z
A
- Acquisition fee – Fee that the bank charges you for the privilege of getting a car lease. The fee varies from institution to institution and usually costs anywhere from $400 to $795; it is also known as a bank fee
- Advertising Association Fee – Fee that dealerships pay to belong to certain advertising associations; it is generally listed on the invoice for a vehicle
- Applied interest – Rate of interest a lender uses to calculate how much you owe
- Asking price – Amount the dealer is advertising the car to be sold at; also known as the sticker price
B
- Bank fee – Fee that the bank charges you for the privilege of getting a car lease. The fee varies from institution to institution and usually costs anywhere from $400 to $795; it is also known as an acquisition fee
- Base price – Cost of a vehicle before any add-ons and upgrades are included
- Blue Book – Guide to pricing that is used by most dealerships to determine the value of a used vehicle
- Bumper to bumper coverage – Type of warranty that applies to virtually all of the parts of a vehicle; read the specifics of the lease to find out what might be excluded
C
- Cap cost – Slang term for capitalized cost
- Capitalized cost – Amount of money that you are financing through a lease agreement, it is calculated by subtracting your down payment from the selling price of the vehicle
- Capitalized cost reduction – This term refers to your down payment, the amount that is subtracted from the selling price of the vehicle to determine the amount that is going to be financed, or the capitalized cost
- Captive Lease Company – Financial institution owned by the automaker that provides leases for their vehicles only; usually the cost to lease cars is less with the captive lease company because they have a direct incentive to get vehicles leased
- CARFAX Report – Detailed history of a vehicle that is compiled using the VIN number for the vehicle (See carfax.com)
- Certificate of title – Declaration of who a vehicle belongs to written by a law office or title company
- Closed end lease – Lease that does not require you to buy the vehicle at the end; you can if you wish to, but you are not obligated to do so
- Consumer Leasing Act – Federal regulation that requires all financial institutions to provide you with the full list of costs for a car lease; also known as Regulation M. (To read more, see ftc.gov)

D
- Dealer incentive – Programs automakers offer to encourage auto salesmen to sell and lease their vehicles
- Dealer preparation fee – Fee that the dealership charges for getting a vehicle ready for you to pick up, which usually is for cleaning the car and filling the gas tank
- Default charge – Penalty that is assessed if you are late making a lease payment
- Deficiency – Difference between the amount that you owe on a lease and the value of the vehicle at the present time; a big deficiency could mean that you would be out money if you are ever in an accident; gap insurance is used to protect lessees from deficiency
- Depreciation fee – Part of a monthly lease payment that is designed to make up for the loss of value of the vehicle that occurred during the month; the residual value is used to calculate the fee
- Destination charge – Fee assessed if a lease vehicle is moved from another dealership to your dealership for you to lease
- Disposition fee – Fee charged by the bank at the end of the lease for the privilege of having been able to lease a vehicle; if you lease another vehicle through the same bank this fee may be waived; it is also called the termination fee
- Drive off fee – Amount of money that you need to have on hand when you sign the lease in order to drive away with the vehicle; usually, the amount is the first payment plus a security deposit, the acquisition fee, and other fees or taxes that your state requires you to pay; it is also called a due at signing or inception fee
- Due at signing – Amount of money that you need to have on hand when you sign the lease in order to drive away with the vehicle; usually, the amount is the first payment plus a security deposit, the acquisition fee, and other fees or taxes that your state requires you to pay; it is also called a drive off fee or inception fee

E
- Early termination – Ending a lease early will usually result in a fee, called an early termination fee
- Effective Annual Rate – Annual percentage rate charged to the lease agreement; it is the money factor multiplied by 2400.
"The APR can also be represented by a money factor (also known as the lease factor, lease rate, or factor). The money factor is usually given as a decimal, for example .0030. To find the equivalent APR, the money factor is multiplied by 2400. A money factor of .0030 is equivalent to a monthly interest rate of 0.6% and an APR of 7.2%." – Reference wikipedia.org
- Equity – Value of a car compared to how much you owe on it; the difference is the equity in the vehicle
- Excess wear and tear – Damage to a car beyond the ordinary expected wear and tear. The bank determines what qualifies as acceptable wear and tear on a lease vehicle; if your leased vehicle has more wear and tear than what the bank allows for, you will be charged a fee for excess wear and tear. Check with the financial institution issuing your lease for the specific guidelines regarding what constitutes excessive wear and tear
- Extended warranty – Extra coverage against manufacturing defects that goes beyond the manufacturer’s warranty; it usually costs extra and is typically not needed for a lease
- Extension – Agreement to continue to make lease payments for a certain length of time beyond the original term of the car lease

F
- F & I – Short for finance and insurance; the part of a car dealership that handles leasing and financing
- FICO Score – Technical name for your credit score, a measure of your credit worthiness; it is used to determine what type of car lease specials you can qualify for
G
- Gap insurance – Coverage that will pay the difference between what your insurance company will pay and the cost of replacing a vehicle, if your car is totaled in an accident or is stolen and cannot be recovered; some financial institutions provide free gap coverage, and if yours does not, you should consider buying it separately
- Gross Capitalized cost – Price of the vehicle that you negotiate with the dealer, which includes any taxes and any other fees that you decide to add into the lease agreement
I
- Inception – The start of the lease
- Inception fee – Fee that must be paid at the start of the lease; usually, the amount is the first payment plus a security deposit, the acquisition fee, and other fees or taxes that your state requires you to pay; it is also called the Drive off fee or Due at signing
- Indemnity – Lease provision that prevents the leasing company from being responsible for tickets or costs due to accidents that you incur as a driver
- Implied interest – Amount of your monthly payment not including the cost of depreciation; it is calculated with the money factor
- Invoice price – Published amount that the dealership claims to pay to add a vehicle to their lot; in reality, the actual cost for the dealership is around 2 percent less

L
- Lease fee – Amount of your monthly payment not including the cost of depreciation that is calculated with the money factor; also known as Rent charge
- Lessee – Person who is leasing the vehicle; you
- Lessor – Financial institution that is granting the lease
M
- Margin – Difference between what the dealership pays for the car and how much they sell it for; this is what provides the dealership with profits
- Mileage Allowance – Maximum number of miles that you are allowed to drive your vehicle every year to avoid paying a penalty; most leases allow for 10,000 miles, 12,000 miles or 15,000 miles
- Money factor – Factor that is used to calculate the amount of interest paid on each vehicle lease. It is a five-digit decimal number, such as .00355; you can find out what the interest rate is by multiplying the money factor by 2400
- MSRP – Abbreviation for Manufacturer’s Suggested Retail Price; it is the sticker price of a vehicle with no discounts or deals
O
- Open end lease – Lease that requires you to pay the deficiency between the car’s value and the amount of the lease; rarely used anymore because they are costly and generally unfair to the lessee
P
- Pre-Approval – When a financial institution promises to grant you a lease on any vehicle up to a certain dollar amount
- Purchase option – Lease term that gives you the ability to buy a vehicle when your lease is finished for the price stated in the leasing agreement
- Prep fee – Another word for the dealer preparation fee
R
- Rebate – Refund of a certain percentage of the money paid for a leased vehicle that is given back to you after the lease is in place
- Regulation M – Federal regulation that requires all financial institutions to provide you with the full list of costs for a car lease; also known as the Consumer Lease Act
- Rent charge – Amount of your monthly payment not including the cost of depreciation, which is calculated with the money factor; and also known as Lease fee
- Residual Value – Figure used to calculate the amount that you would pay at the end of a lease to buy the vehicle; it is expressed in a percentage and is multiplied by the Manufacturer’s Suggested Retail Price of the vehicle; banks also use the number to determine how much depreciation to include in lease payments
- Repossession – When the financial institution takes back a vehicle because a lease is severely past due

S
- Sales Tax – Fee paid to the state equal to a percentage of your lease payments; it is called use tax in some states
- Security Deposit – Fee that a dealership requires you to pay when you lease a vehicle; normally, it is equal to one month’s lease payment rounded up to the nearest $20 or $50; if you pay extra, you may be able to get a discount on the money factor
- Service contract – Agreement that allows you to pay a fee upfront in exchange for discounted service at a dealership’s maintenance center in the future
- Single payment release – Leasing agreement that allows you to pay the lease fees and payments up front at the start of the lease in one lump sum, so that you never have to make a monthly payment
- Spiff – Incentives that encourage car salesmen to lease vehicles
- Sticker price – Amount the dealer is advertising the car to be sold at; also known as the asking price
- Subsidized lease – Lease from the captive lease company that has a high money value, or a lower money factor to make for a great car lease deal; also known as a subvented lease.
- Subvented lease – Lease from the captive lease company that has a high money value or a lower money factor to make for a great car lease deal; also known as a subsidized lease
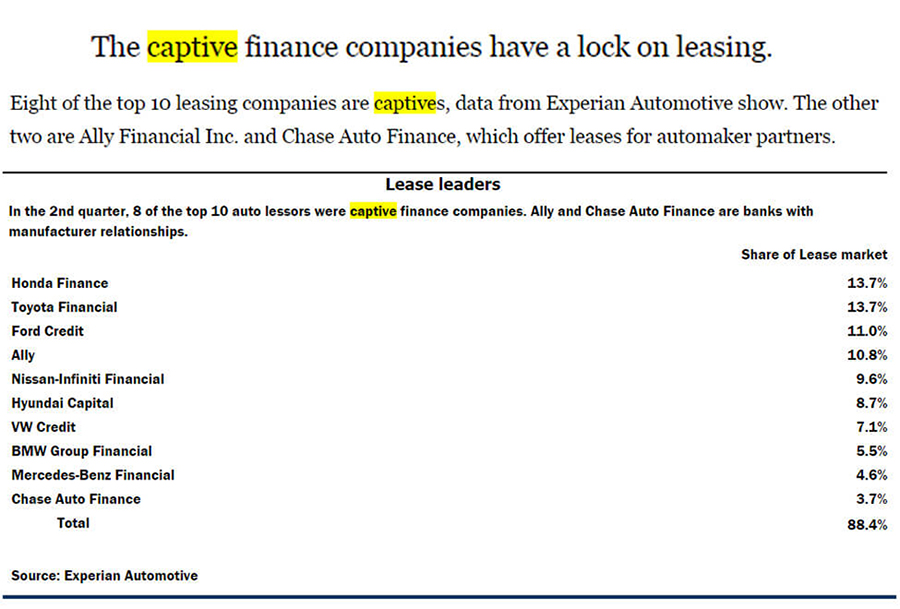
"Why are captives the lease leaders? For one thing, they are more motivated to push leasing than banks or credit unions because leasing encourages brand and dealership loyalty. They also have more appetite for the risk inherent in leasing related to residual values. And unlike most banks, the captives, their manufacturer parents and their dealer networks are geared for remarketing lease returns." – Quote & Photo credit: AutoNews.com
T
- Term – How long the car lease lasts; most leases are 24 months, 36 months, or 47 months; usually a short term lease will have a larger payment than a long term lease
- Termination fee – Fee charged by the bank at the end of the lease for the privilege of being able to lease a vehicle; if you lease another vehicle through the same bank this fee may be waived; also called the disposition fee
- Title – Paper that signifies who owns a particular vehicle
- Trade-in value – Value of an old vehicle that you wish to trade into the dealership; the amount is deducted from the capital costs of the lease

U
- Upside Down – Term meaning that a person owes more on a lease than a car is worth
- Use tax – Fee paid to the state equal to a percentage of your lease payments; it is called sales tax in some states
V
- VIN – Abbreviation for vehicle identification number; a one-of-a-kind number issued to every vehicle, which is used to track information about the car
W
- Warranty – Agreement that says the manufacturer or a third-party will cover repairs to certain parts of a vehicle for a set length of time. Make sure you know your Lemon Law rights under the state law, please see dmv.org
There you have it–the most common car lease terms that you need to know before you go to the dealership. Bookmark This Page [Press Ctrl+D together to add to bookmark] so that you can reach it quickly if you encounter any unfamiliar terms when you start to read lease agreements.
